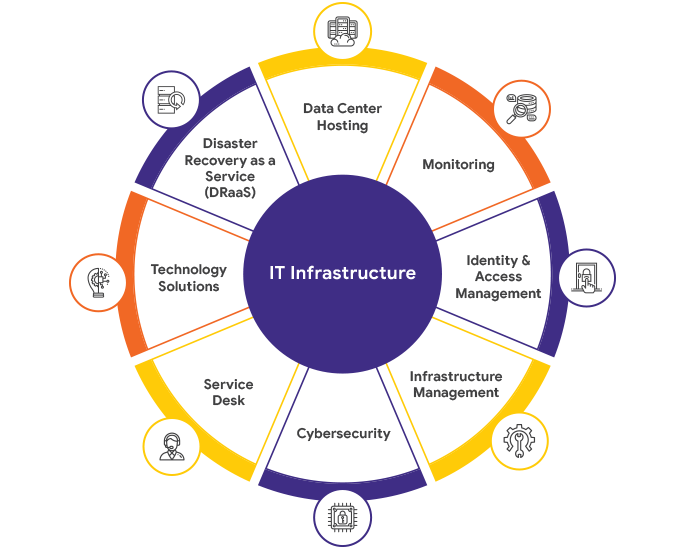
Introduction:
When we think of the term “infrastructure,” we often associate it with roads, bridges, and buildings. However, infrastructure encompasses much more than physical structures. It forms the backbone of modern societies, providing essential services and systems that enable economic growth, connectivity, and overall development. In this blog, we will delve into the basics of infrastructure, explore its various forms, and highlight the numerous benefits it offers.
Defining Infrastructure:
Infrastructure refers to the fundamental facilities, systems, and structures necessary for the functioning of a society or organisation. It encompasses both tangible and intangible assets that support various sectors, such as transportation, communication, energy, water supply, healthcare, education, and public services. Infrastructure includes physical assets like roads, railways, airports, ports, power plants, and also intangible components like information networks, software systems, and institutional frameworks.
Types of Infrastructure:
1. Transportation Infrastructure: This includes roads, bridges, railways, airports, seaports, and public transit systems. Efficient transportation infrastructure facilitates the movement of goods, services, and people, boosting trade, tourism, and economic activity. Click here for more details
2. Communication Infrastructure: It comprises telecommunication networks, internet connectivity, broadcasting systems, and data centers. Robust communication infrastructure fosters information sharing, enables remote collaboration, and supports the growth of businesses and digital economies in secure way.
3. Energy Infrastructure: This category encompasses power generation plants, electrical grids, pipelines, and renewable energy installations. Reliable and sustainable energy infrastructure is essential for meeting the increasing demands of industries, households, and technological advancements. For more information, click here
4. Water and Sanitation Infrastructure: It includes water supply networks, wastewater treatment facilities, dams, and reservoirs. Access to clean water and proper sanitation facilities is crucial for public health, hygiene, and overall well-being. For more details, look at here
5. Social Infrastructure: This refers to facilities like schools, hospitals, public libraries, community centers, and recreational spaces. Social infrastructure plays a vital role in providing education, healthcare, cultural enrichment, and social cohesion.

Benefits of Infrastructure:
1. Economic Growth: Well-developed infrastructure contributes significantly to economic growth and productivity. It facilitates the efficient movement of goods and services, reduces transportation costs, and attracts investments. By connecting regions and markets, infrastructure enhances trade and stimulates business activity, leading to job creation and increased prosperity.
2. Improved Connectivity: Infrastructure networks, such as transportation and communication systems, enhance connectivity within and between communities. They promote accessibility, reduce travel times, and foster social interactions. Improved connectivity also expands market reach, encourages tourism, and supports the development of rural and remote areas.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life: Infrastructure development directly impacts the quality of life for individuals. Accessible healthcare facilities, reliable power supply, clean water, and efficient transportation services improve living conditions and contribute to overall well-being. Social infrastructure, including schools and libraries, provides opportunities for education and personal growth.
4. Sustainable Development: Infrastructure can be designed and implemented with sustainability in mind. Green energy projects, efficient public transportation systems, and eco-friendly waste management initiatives contribute to environmental sustainability. Well-planned infrastructure development also considers social equity, ensuring that all communities benefit from its advantages.
5. Resilience and Disaster Management: Robust infrastructure systems play a crucial role in disaster management and resilience. Well-constructed buildings, robust communication networks, and effective transportation systems help mitigate the impact of natural disasters and ensure swift emergency response.
Conclusion:
Infrastructure is the foundation on which modern societies thrive and progress. It encompasses a wide range of sectors and services that support economic development, connectivity, and improved living conditions. By investing in infrastructure, governments, organisations, and communities can unlock significant benefits such as economic growth, improved connectivity, enhanced quality of life, sustainable development, and resilience. Recognising the importance of infrastructure and working.